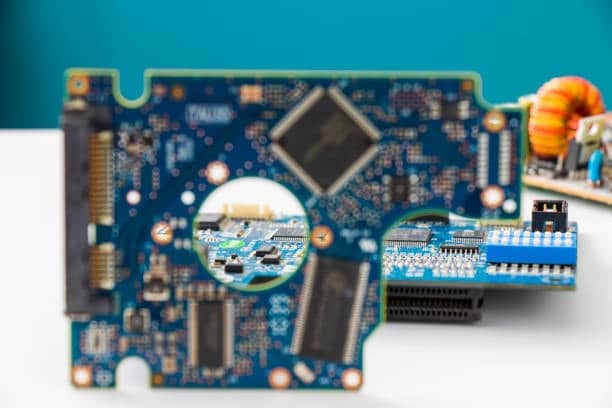
Unveil the critical features and guidelines for the various advantages of quick and easy printed circuit board, boards and PCB boards prototyping in this easy-to-understand guide. Understand how to design the PCB boards and prototypes specifically for efficient advancement and guarantee success rate capabilities.
What is Rapid PCB prototyping?
Rapid PCB prototyping denotes the quick-turn pcb prototyping modeling phase aimed at building a working prototype as fast as possible for testing and validation. This approach allows those who work with machinery and layout systems to reiterate faster and more efficiently; hence, the progress time frames for electric devices and consumer electronics are shortened
What are the benefits of Rapid PCB Prototypes?
The advantages and many benefits of fast proofing of PCBs become obvious at the product growth stage, which improves overall effectiveness of resources and results in a cost-effective, faster time to market. Here are the list of advantages:
Quick Turnaround Time
speed of mock-up processes enables manufacturers to go from design concept to real prototype in a very short lead time, which minimizes the overall time to market. This competitive advantage, in turn, accelerates the method of iterating through the design files material, hence fostering the overall design file evolution procedure.
Faster Time to Market

Through rapid prototyping capabilities, manufacturers shorten the time needed to bring new products to the market, which makes the total time frame even shorter. These abilities are especially helpful for enterprises and companies that try to be one of the first on the market because this can grant companies a powerful competitive advantage.
Cost Savings
Physical modeling diminishes the demand for labor and the cost of obsolete production re-running equipment and costly faults at late production finishing. Besides, shorter development cycles lead to lower labor costs and eventually cost efficiency improvements.
Iterative Design Process

The capacity to iteratively test and improve many designs in a short time with PCB Prototyping ensures that the design process becomes faster and more stable. This iterative workflow will enable a review of the final product to ensure its ability to meet the given design requirements. This may include optimization for speed, functionality, and ease of manufacture.
Reduced Risk
Using prototyping for rapid concept verification helps businesses manage and reduce the risks of product development. Find and correct problems in the beginning; it simplifies the procedure for catching expensive mistakes or delays in the project.
Flexibility and Customization
With rapid prototyping techniques, engineers can have flexibility and options for customization. These adjustments enable us to try different materials, approaches to component fabrication, materials, manufacturing processes, and design configurations to enhance performance and satisfy the particular requirements of the project.
Improved Collaboration
Fast PCB prototyping opens access to all people from different departments, such as design engineers, component manufacturers, and even stakeholders, to work together. By presenting prototypes in a visible form during the prototype launch stage, teams create a shared understanding about the project goals, design rules and specifications.
Enhanced Innovation
The feature of trying and affirming prototype boards of different types very quickly promotes innovativeness and a creative way of solving problems. The fast pace of the development cycle and the mock-up procedure allow engineers to test out new concepts and make them work beyond what is possible, thus facilitating inventions in design, functionality, mass production, and other relevant aspects of product creation.
In brief, fast-printed circuit board (PCB) prototyping provides all sorts of advantages that turn the cycle of product development into a more effective, less expensive, flexible, and time-saving procedure, thus resulting in the creation of good products.
Why use Rigid-Flex PCB in rapid prototyping?
Rigid-flex PCBs offer several advantages that make them very flexible and ideal for rapid fabrication and prototyping in support of various electronic component applications:
- Space Optimization: Rigid-flex PCBs offer compact designs due to their combined rigid and flex wiring systems on a single board. It also reduces overall size and enables the use of more space inside the prototype, which is very important for minimizing the size of electronic devices aimed at compactness and portability.
- Design Flexibility: The flexibility of combining rigid and flexible sections enables designers to get a wider creative space in comparison to PCBs with only rigid circuitry. Designers may utilize complicated forms and three-dimensional patterns to accommodate unusual form-factors which are found in prototyping and also to challenge light-out layout demands.
- Reduced Assembly Time: The rigid flex PCB helps to reduce the number of interconnections and connectors between multiple rigid boards, thereby making the assembly method simple. This speeds up assembly, eliminates the number of welding points, and cuts down manual labor, consequently expanding the prototyping method.
- Enhanced Reliability: Based on the concept of flexible-rigid printed circuit boards (PCBs), there are fewer interconnections, which decreases the probability of contact failure and intermittent connections, a common problem in assembly with many connectors and cables. This has a high degree of consistency and long-term durability, which are necessary components for successful testing and evaluation of the prototype.
- Improved Signal Integrity: The main advantage of rigid-flex PCBs is the reduction of the use of connectors and cables, which ensure the minimization of signal degradation and electromagnetic interference (EMI). It is a prerequisite for better signal quality and noiselessness, which are essential in the precise testing and verification of electronics during the developmental phase.
- Cost Efficiency: Where the initial prototype development may be costlier due to specialized material fabrication, rigid-flex PCBs may still lead to overall cost reduction in the long run. These qualities mutually entangle to cut operation expenses such as repayments and replacements of parts while speeding up the workflow of product design and reducing product development costs.
Also, the possibility of baking rigid-flex printed circuit boards (PCBs) in the rapid prototyping method creates various advantages, such as space optimization, design flexibility, minimized assembly lead time, enhanced reliability, great signal integrity, and cost-efficiency, which makes them a great choice for quickly prototyping and testing electronic prototypes in small quantities.
Best Practices for Rapid PCB Prototyping

These are the best practices for rapid pcb prototyping:
1. Define Clear Objectives
Know Your Aim Before you go ahead with the prototyping step, ensure that you have well understood and established your goals and the standards of your project. By understanding such specifics, for example, we are able to define the interfaces, measures of performance key features, and limitations necessary during the processes of design and prototyping.
2. Choose the Right Tools and Software
Select & Use Appropriate Tools & Software In PCB design, select and use tools and software which support rapid prototyping. Computer tools, such as those that allow designers to work on boards in real-time concurrently, flexible component libraries, and automated design rule check tools, can go a long way in making the process easier and eliminating mistakes.
3. Select Suitable Materials and Components
Choose the appropriate material, technology and parts Both for exterior and interior, some kinds of materials and parts are chosen in essence of making a prototype. Taking into account signal integrity criteria as well as thermal and mechanical performance characteristics. Closely collaborate with suppliers to secure sustainable delivery, production and purchase of the right components.
4. Collaborate with a Reliable PCB Manufacturer
Need for Choosing a Reliable PCB Manufacturer Working with a professional and fast-turn PCB manufacturer can go a long way. Also, always ensure to look at the company’s very quick turn-around time for prototypes, the sophistication of the fabrication capacity and the quality of the things that the particular manufacturer in question offers to its customers in the prototyping business.
5. Iterate and Test Thoroughly
It also instructs that rapid prototyping is an iterative process that needs to be tested rigorously In this context, the article is instructive about the underlying nature of rapid prototyping as an iterative process that has to be tested rigorously. In testing each of the prototypes, C should ensure that data is collected on how the actual prototype is functioning in comparison to the expected behavior and try to fix and modify any issues as they devise the final prototype to be used in testing. Do not skip many iterations or cycles; always make sure that each developed change is tested to the proper extent in order to meet the specifications of the final product in question.
6. Document the Process
As is the practice when undertaking observations, the whole process of prototyping should be recorded in detail. For record design changes, test results, or any problems experienced in the process of record design, these should be documented as well. They will also be very helpful in the future when subsequent prototypes are made, as it can help troubleshoot and fix issues.
7. Focus on Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
Design for Manufacturing Just remember, while you are building the first prototype, it has to be designed to be manufactured. Make sure that it is easy to produce it for commercial purposes, given that the design is creative and effective . It is important to take into consideration factors such as how the assembled product will be produced, how testing will be done, and how the product will scale during the production run during the manufacturing process in order to prevent problems from arising.
Conclusion
At the end, it can be commonly agreed that fast PCB prototyping, or rapid PCB, is an extremely powerful mechanism in the world of PCB manufacturing, containing unbeatable properties like speed, flexibility, reducing process costs, and minimizing risks. With a rapid pace, the prototyping process enables the production of 3D-printed parts that never entered the market before, shortening the time to market. Furthermore, rapid prototyping can facilitate rapid iteration and reduce costs for small-scale productions, bringing designers closer to their customers for PCB services.
Integration of modern manufacturing technologies gives rise to smart universality, which opens up a new world of customization, personalization services, and rapid delivery of advanced electronic products and services. Today, rapid PCB prototyping can be considered the backbone of modern product development. Not only does the development process become faster but it also has the ability to deliver high-quality, reliable solutions and services to the market in a timely and flexible manner without sacrificing quality.