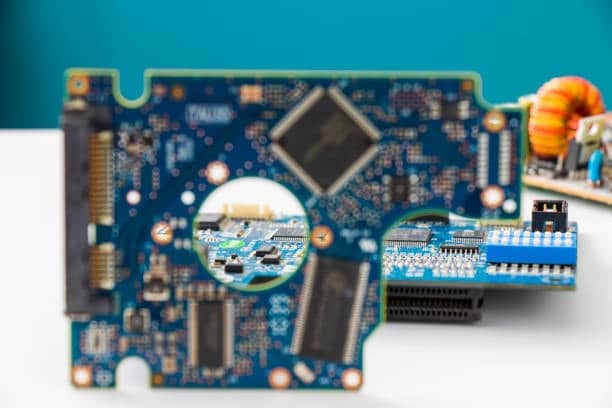
PCB testing and inspection include different methods to test if the PCB is up to the standards. Some of these PCB standards revolve around ensuring that the PCB is functional as per the project requirements with no defects.
What is pcb testing and what is being tested?
Printed circuit board testing is popularly known as PCB testing which is the procedure of evaluating the workability and integrity of a printed circuit board (PCB) that forms a base for majority of electronic devices. However, in testing, a variety of features are assessed – among others the electrical connection, the accuracy in placing components and the compliance with design criteria.
Such a process ensures that the PCB is usable and functioning properly and reliably within the intended electronic system. In this sense, some of the actual testing methods involve automated optical inspection (AOI), in-circuit testing (ICT), and functional testing which may be used to verify that the printed circuit board (PCB) meets the quality standards and operates as desired.
Seven types of pcb testing methods
You can read each details and explanation for the seven types of PCB testing methods:
1. Automated optical inspection (AOI) testing methods
One of the techniques used at the AOI step involves cameras and image processing algorithms which are used to detect faults in printed circuit boards (PCBs). Such defects include lack of components, wrong placements, missing soldering, and shorts.
2. In circuit testing of pcb testing methods
The process of testing individual components and connections on a printed circuit board which is also known as ICT is the method of In-Circuit Testing. This function checks the circuit for a number of faults among them open circuits, short circuits, faulty component values and others.
3. Functional testing testing methods
This approach is employed in the evaluation of performance of printed circuit board which is characterized by the application of input stimulation and output observation on PCB burn in testing.
4. X-ray inspection testing methods
X-ray inspection provides advanced visualization of PCB interior structures. Such action enables the recognition of failures including the masked solder connections, voids, and misalignments of components, especially to some extent in multi-layered assemblies burn in testing.
5. Boundary scan testing methods
Boundary scan testing is a technique which assesses the validity of interconnections as well as determines the functioning of digital integrated circuits burn in testing. It is by scanning and modifying the given pins’ active states at the instance of circuit testing.
6. Flying probe testing methods
Flying probe testing is one way of testing printed circuit boards (PCBs) that does away with the necessity of using dedicated test equipment substituting it all to use automated probes pcb functional testing.
To test whether there is connection, shorts, or opening across the board the probes are moved around different test spots on the board.
7. Environmental testing methods
Environmental testing of printed circuit boards (PCBs) includes exposures to extreme environments such as heat, humidity, vibration and thermal cycling to check upon their reliability and performance under natural operating environment. Using this technology, future-failure due to environmental stresses can be detected.
How to protect the pcb with better designs?
What can be done to improve component location so as to eliminate heat collection and interference in a bid to enhance PCB protection via better design. To balance the voltage and reduce noise researcher suggests regarding these solid ground and power planes.
Secondly, protective procedures that prevent electromagnetic and radio frequency interferes need to be adopted.
Trace routing needs to be SIGNAL INTEGRITY and IMPERANCE MATCHING OPTIMIZED and PROTECTIVE CIRCUITRY included to provide PROTECTION FROM ELECTRICAL FAULTS and TRANSIENT EVENTS. Water damage or dust, both due to overheating becomes a mute point only when the efficient thermal management systems coupled with environment sealing methods are employed.
The confluence of all these design principles, therefore, enhance the dependability and longevity of printed circuit boards (PCBs) in electronic systems.
Three types of design for manufacturing
There are the three types of design for manufacturing process read the details below:
1. Design for assembly (DFA) :
represents one of the approaches that deals with idea of better product design which allows improving the ease of production of the product assembly, which, opinion assembles it, it should be cheaper.
For this to happen, the number of parts should be reduced, the assembly process refined and specialist tools and equipment has to be avoided.
2. Design for testability (DFT)
is a methodology which is aimed at streamlining the process of testing and inspection that is embedded within the production process. Along this procedure, fraud is caught as goods are formulated to possess certain traits by which makes it easy to test avoiding tampering –unlawful.
Such characteristics are built-in test points, diagnostic capabilities and self-test routines that facilitate problem identification and product quality maintenance.
3. Design for Reliability (DFR)
To reduce failure and maintenance demand that goods under consideration would require during its life period DFR provides products with significant robustness and reliability components.
It includes qualifying selected components, adequate heat dissipation provision, incorporating redundant systems where necessary, and beginnings the reliability testing phase to detect and then solve potential failure modes at the early stage of the design process.
Advantages of functional testing
- Ensures Product Integrity– Function testing ensures that product will work correctly and consistently as per functions it is designed to perform.
- Early Defect Detection – The method not only detects defects at an early stage of production but it also helps to reduce the time involved during rework or recall of the products.
- Quality Control – This function helps in maintaining the quality standards consistently by eliminating non-complying goods based on the criteria.
- Enhances Reliability – This function helps to detect potential sources of reliability issues that make products durable and trustworthy.
- Optimizes Efficiency – This feature makes the production processes easy and cut down on the manufacturing cost since it aims at reducing delays in the production process.
Why is the pcb testing is essential?
There are a few reasons that make PCB testing an indispensable component. For starters, it ensures that the printed circuit board functions well within the electronic system in which it is designed and as such, ensures that the device delivers appropriate results. Any errors or flaws in the printed circuit board (PCB) can be detected through testing were manual visual inspection.
This can be things such as soldering mistakes, problems during placement of the components, and connection errors, all of which risk breaking or malfunctioning the final product to the printed circuit boards just to have test fixture.
PCB testing enables engineers to mitigate losses associated with expensive rework, waste and faulty product recalls by identifying the problems early enough in the manufacturing process. This leads to higher production efficiency and low costs of production. Besides, PCB testing serves as a crucial element in the quality and reliability preservation process.
This is due to the fact that it guarantees that the product meets design requirements and industry requirements that in the long run help in creating high levels of consumer satisfaction and brand reputation.
Mechanical pcb testing and inspection tool
Mechanical PCB testing and inspection tools are required essential equipment for assessing the physical integrity and performance of printed circuit boards (PCBs), which are used in the manufacturing and quality assurance processes. This assortment of equipment includes the AOI machines, the X-ray inspection systems and the flying probe testers, and other apparatus for the circuit board test qualifications in manual visual inspection.
They help in the identification of defects like soldering issues, component misalignment, and physical damage to ensure that printed circuit boards (PCBs) meet the strict quality standards and design specifications. Mechanical testing and inspection tools allow manufacturers to perform detailed analysis and broaden the examination of printed circuit boards (PCBs), which helps to reveal and correct anomalies before the end of the manufacturing process.
This also decreases the volume of costly corrections and increases the product’s overall realiability and consistency.
Electrical pcb testing during manufacturing process
The PCB electrical testing is a critical step that should be taken from within the manufacturing procedure to ensure the functionality, quality, and efficiency of the printed circuit boards (PCB). In an electrical testing process, checks are made on the integrity of the electrical connections as well as the accuracy of component placement and design criteria for the test method in testing procedures.
These techniques use various methods such as in-circuit testing, automated optical inspection, and also functional testing to bring out the required results. Components and circuits in the ICT component are inspected for electrical faults including open circuits, shorts, and incorrect component values for the final quality control procedure to the functional test.
However, AOI puts visual inspection into action to bring to light issues like lost elements, bad soldering, and misalignments. When it comes to functional testing, performance of the printed circuit board (PCB) is determined by subjecting it to consolidated working scenarios through simulation.
This guarantees that the PCB operates in the way it was meant to. By performing these sophisticated electrical tests, the manufacturers can catch the defects even before they leave the factory as a product in pcb assembly testing types. This leads to a reduction in the rework needed, an improvement in product quality, and satisfaction of the customers.
Reliability and pcb failure analysis
Reliability and PCB failure analysis play an important role in ensuring the integrity and longevity of PCBs in electronic devices. Reliability refers to the capability of a printed circuit board (PCB) to perform the activities it was meant to perform, and have been designed to do in a repetitive manner throughout its entire useful life in those electronics manufacturing industry some have very load capacity and automated x ray inspection. A PCB failure analysis is an assessment of the root cause of the failures or malfunctions of the printed circuit boards.
These can be a result of a number of factors such as design flaws, production errors, environmental stresses, or operation factors pcb functional test which will have test load capacity or other testing methods. Performing comprehensive failure analysis helps Manufacturers to identify the underlying issues that lead to printed circuit board (PCB) failures, address corrective actions it will detect early failures, and the improvement of the design and manufacturing processes to increase the overall reliability of their products with specialized equipment with missing components for PCB quality to other functional tests.
This prediction strategycut make it less likely that mistakes will occur in the future, lower the number ofproduct warranty claims, and maintain customer confidence on the reliability and reliability ofelectronic equipment human error.
Benefits of pcb testing
The PCB testing has many advantages that are important to the manufacturing process and product quality of their chip components and have visual inspection on those electrical signals to the electronic circuit. To begin with, it ensures that the printed circuit boards (PCBs) conform to necessary requirements by putting their functionality and dependability to test and have testing limit to the . Early detection of defects can prevent their distribution into the market which in turn brings down on warranty claims and return of products.
Moreover, timely discovery of problems by printed circuit board testing enhances manufacturing efficiency thereby decreasing costly rework time and delays. The profit margins increase due to printed circuit board (PCB) testing since it ensures that there will not be any potential failures in production so as to improve customers’ satisfaction as well as maintain a good image for the company. On the whole, this is a critical phase in production because it guarantees reliable functioning of electronic appliances according to acceptable standards.