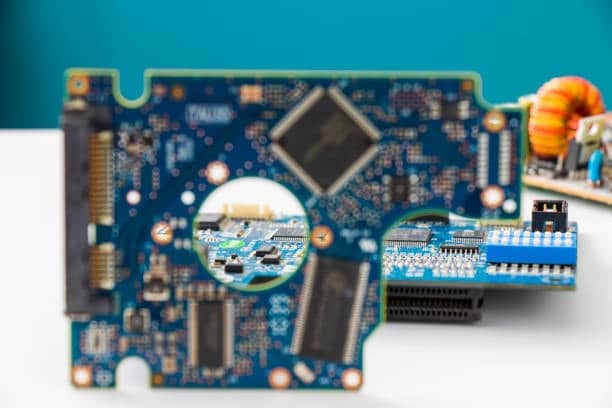
Printed circuit boards are the foundational item of the modern day electronics and they act as the pathway that links some of the units. Copper has long dominated the use of gold in electronics and the manufacturing of circuit boards because of its high conductivity and moderation in price compared to other metals, however, silver printed circuit boards are seen to be a better solution in some instances. This blog will illustrate various aspects of silver circuit boards including the benefits associated with them, process of manufacturing the silver circuit boards, uses of the silver circuit boards and prospects in the future.
What is immersion silver PCB?

An immersion silver PCB is a type of PCB where the surface of copper is painted with a thin layer of silver through a chemical dip. On top of this copper layer is a layer of silver which is used mostly as a finish; it provides excellent conductivity and is easily solderable and it’s major role would be to prevent the copper from oxidising and tarnishing. While immersion silver is often preferred for its smooth and flat surface which is well suitable for processing of fine-pitch components and Surface Mount Technology (SMT).

Furthermore, it has good electrical characteristics; thus, it is suitable for high frequency and high speed. This finish is also free of lead and hence is an eco-friendly product that complies with the RoHS standards among other statutes.
Why Silver? The Unique Advantages
The unique advantages:
1. Superior Conductivity
Silver tops the list in conducting electricity, even surpassing copper, although fairly closely. This indicates that, in the application of high performance circuits; there is an opportunity to achieve higher signal speed and minimized power loss through the use of silver circuit boards.
2. Thermal Conductivity
Argentum also has good thermal conductivity and effectively removes heat produced by electronic elements. This property aids in the sustaining of efficacy as well as durability of the devices especially in the high power usage.
3. Corrosion Resistance
Unlike copper that will over time tend to rust and thereby deterioriate, silver has a more noble disposition and will not easily oxidize. This make silver circuit boards more durable and reliable especially in environments that are unforgiving to some other circuit boards.
4. Mechanical Properties
Silver is for more pliable and easy to shape when hammered compared to copper. This results in much better design control of the circuit boards; more miniaturization can be employed, and more complex geometries are achievable.
Manufacturing Process of Silver Circuit Boards
Manufacturing process of silver circuit boards:
Material Sourcing and Preparation
The first step is procuring the raw material, which in this case pristine silver. Subsequently, the silver is purified before it can be deposited on the substrate of the circuit board.
Substrate Preparation
Copper circuit boards: the standards are brass, ceramic, platinum and mainly PTFE commonly matching silver due to compatibility aspect.
Silver Deposition
Ag can be deposited by many techniques like electroplating, acid sputtering or chemical vapor deposition. Each of the methods has its pros, which is why the choice of the method depends on the application’s characteristics.
Patterning
After forming the silver layer, the selected pattern may be produced by photolithography or laser etching on the surface. It enables high precise and resolution that are desirable in today’s advanced electronic designs.
Etching and Cleaning
After that, if there is remaining silver, the board undergoes etching to eliminate it and then rinsed again in order to eliminate bottoms and other impurities.
Quality Control and Testing
Several tests are performed for the assessment of the quality and efficiency of the silver circuit boards. This comprises electrical inspection testing, thermal tests, and mechanical surveys.
Comparing Silver and Copper Circuit Boards
Comparing Silver and Copper Circuit Boards:
Electrical Performance
Although copper provide good connection property, than silver does better than copper with signal transmission and less resistance.
Cost Considerations
Silver is more costly than copper and this is a disadvantage since it may hamper the calibration of the instrument in use. But in higher performance and critical applications the advantages can definitely overcome the disadvantage.
Durability and Longevity
Oxidation and corrosion are significant challenges in many applications, and thus silver’s high resistance to them entails that it is on average almost permanently superior to other metals in durability and useful life, depending on its specific application.
Application Suitability
Thus, it can be seen that the silver circuit boards are ideal for usage in high frequency and high power requirement areas such aerospace, military and modem telecommunication applications.
Applications of Silver Circuit Boards for electronic devices
These are the applications of silver circuit board
Aerospace and Defense
The electronics industry needs ceramics that can, at the same time, the aerospace and defense industries need components that can endure harsh conditions. Actual silver printed circuit boards are utilized in many systems or sub systems such as radar, communication and navigation.
Medical Devices
With applications in highly sensitive medical devices, the use of silver printed circuit boards results in the highest standards of efficiency. These crystals are incorporated into diagnostic instruments, imaging appliances, and wearable health care equipment.
High-Frequency Telecommunications
Silver’s conductivity also offers signal frequency capabilities that making telecommunications equipment like 5G mobile phone and satellite equipment favorable for use with the material.
Automotive Industry
With the progressive improvement of car models that come with integrated electronics, more gold uses of silver circuit boards are seen in such categories as the advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), infotainment, and the power of electric vehicles.
Consumer Electronics
In the areas of smart mobile phones, notebook computers, and wearable devices, which are high-end consumer electronics products, products using the circuit boards made of silver materials can stand better performance and service life.
Common problems and solutions during Immersion Silver
Apart from certain advantages that immersion silver PCBs have over the conventional ones, it has certain manufacturing challenges. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
- Tarnishing and Oxidation
- Problem: Immersion silver is also sensitive to oxidation whenever the board is exposed to air which causes the solderability and the outer look of the PCB to be affected.
- Solution: To avoid causing more harm to the PCBs and/or making them less usable, store them in anti-tarnish bags or vacuum bags or equivalent packaging. In this regard, it is possible to apply an anti-tarnish treatment on the front during the process of manufacturing to shield the silver layer.
- Whisker Growth
- Problem: Silver whiskers, which are thin, metallization like hairs growing on immersion silver PCBs, also poses a problem of short circuit and reliability.
- Solution: By practicing good control on the plating process and preventing the occurrence of stress promoting conditions, whisker growth can be prevented. Daily surveillance by department quality assurance officers and supervisors can assist in identifying and solving such a problem at an early stage.
- Contamination
- Problem: Any type of oil, dust or any other residue that may be present on the PCB surface at this point may interfere with the immersion silver finish.
- Solution: It is necessary to adhere to the best practices when cleaning the PCB surface before applying the immersion silver coating. Doing disinfection properly and using very high purity chemicals can help to acquire a clean surface without contamination nitric acid.
- Poor Adhesion
- Problem: If interfacial adhesion of the silver layer to copper substrate is not good, it begins to peel off or flake off, thus affecting the performance of the board.
- Solution: Proper surface preparation like surface microetching of the copper, or pre-cleaning before the deposition of the silver layer will improve the adhesion of the last layer. Further, the other aspects of immersion process such as the temperature and immersion time the item being treated will also result in better adhesion quality.
- Non-Uniform Coating
- Problem: Positional dependencies of the silver layer thickness cause the issue of solderability and electrical parameters to be unstable.
- Solution: The following is on how to achieve a uniform silver layer: Control of the immersion process parameters is very critical, and should be done with a lot of precision, and by using automated equipment. Proper monitoring from time to time and other process interference guarantees equal thickness of the coat.
- Thermal Stress
- Problem: Tensions from soldering or running can cause the layer of silver to crack or even delaminate.
- Solution: The control of heating profile and proper soldering techniques helps to reduce the amount of thermal stress. Another way of minimizing thermal damage is by deciding on the PCB layout in a such a way that heat is distributed evenly.
- Compatibility Issues
- Problem: Immersion silver does not support well with some trading flux or solder pastes resulting in the poor solder joints on the P.C.B.
- Solution: Therefore, the employment of right fluxes and solder pastes directly applicable for use in immersion silver plating can be effective in soldering electronic scrap.
In a case where one is in doubt regarding which material is compatible with another, one ought to speak to the suppliers of these materials or engage in compatibility check-ups. Thus, it is possible to note that the given issues should be solved with specific approaches, which will help manufacturers to enhance the characteristics of immersion silver PCB and their applicability in a wide range of applications valuable materials.
Challenges and Considerations
Cost effective
That is how much gold why one of the most important factors stands for the higher cost of silver. However, as the technique of manufacturing advanced along the lines and economies of scale achieved, the cost factor seems to reduce.
Material Availability
Silver is however less available than copper, the availability of silver is a bit a problem as far as supply is concerned. The example shows that it is possible to reduce this problem by searching for different types of sources or experimenting with recycling.
Manufacturing Complexity
It has been noted that the process of manufacturing silver circuit boards is more elaborate compared to other circuit boards and entails the use of better equipment and technical knowledge. It is true that the mentioned challenges can be managed through investing in advanced manufacturing technologies.
Future Trends and Innovations in silver circuit board
Future Trends and Innovations in silver circuit board for precious metals:
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology application on the silver circuit boards can improve the product performance and material consumption electronic circuit boards. For instance, silver nanoparticles can be employed to make good electronic inks to be employed in printed circuitries.
Hybrid Materials
To enhance the characteristics of circuit boards other materials can be added to or alloyed with silver including graphene extract gold. These hybrid materials can give your specific application both the performance and the cost effectivity that you are looking for cell phones.
Sustainable Practices
Other Al behaviors, like recycling gold recovery silver from electronic waste, may serve as a solution to the problems related to material availability since they are less environmentally questionable.
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
Innovation such as, the adaptive manufacturing (3D printing) and laser sintering for production of silver circuit boards were also looked at as having the capabilities for better performance.
Why are there precious metals on the PCB?
Interested metals are used on PCBs mainly due to their excellent features such as electrical conductivity, resistance to corrosion as well as high durability. Signal pathways are made of gold, silver, and palladium, these metals are good conductors of electricity hence the signals are transmitted very efficiently with little loss of energy. This is particularly vital in high-performance electronics as the latter requires very high levels of accuracy and reliability. For example, gold is applied to the edge connectors and contact points as it is a non-corrosive metal and does not turn black over time and yet remains a secure connection in adverse conditions. These metals in their usage assist in attaining high performance and excellent life in electrical and electronic devices.
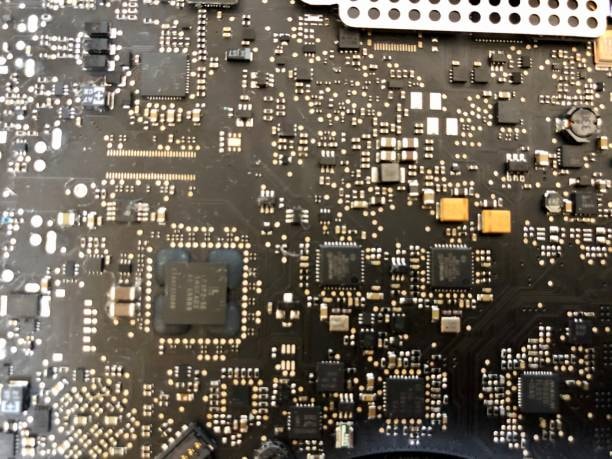

In the same manner, precious metals do enhance the general dependability and solidity of the PCBs. It is for this reason that those Relays can withstand extremely unfavorable operating conditions such as high humidity, high/low temperatures and corrosive environments. This makes them suitable for use in industries that cannot afford to have a flaw and these include aerospace, medical device and telecommunication fields. Besides, incorporation amount of gold precious metals in PCBs also enhance soldering and guarantees that the final product will have strong and durable marrying points which are crucial in the functionality of the electronic assembly. Even though these metals are costly compared to others, they will, in most cases, respond to the high cost by outperforming other materials for high-end and mission-critical applications.
Gold, silver and copper on the PCB
The metals frequently employed in PCBs include gold, silver, and copper because of their proficient electrical characteristics and their applicability due to distinctive features they possess for various functions.
Gold plating
is very important for PCB manufacturing due to high conductivity as well as ability to prevent the board from tarnishing. It is utilized in plateauing of edge connectors, contacts, and key connections where good and stable connections are required. Since gold does not corrode, these connections remain constant and highly functional for high-speed and high dependable use areas like aviation, health arrangements, and communication. Despite the fact that gold products are expensive, this cost should be justified by the resistance of gold and better performance in areas, which are the most significant.
Silver
includes electrical and thermal conductivity with the compound being even better than copper. It’s mostly applied to immersion silver PCBs where a thin coating of silver is plated on the copper fringe to improve solderability and reliability. Hence, silver is especially favorable for high-frequency and high-speed circuits primarily because it betters signal transmission. Further, it has protection against oxidation which would also make it to be very reliable in the long run. Silver, however, is less commonly used as compared to copper because it is expensive; even though it has specific advantages and is ideal for some of the modern applications in electronics.
Copper
is the most preferred metal in the manufacturing of the PCBs due to aspects such as high conductivity, relatively cheap, and ease to work on. It is to be observed that almost all PCBs have copper layers, making up the traces and pads through which the circuits are formed and the components are connected. Thus, copper can be deemed to have a good balance between performance and cost, making it the most preferable in most electronic products. The application of carbon fiber reinforced plastic can been seen in products ranging for small portable electronics gadgets to large machinery and equipment. Although copper circuits are vulnerable to oxidation that is usually curbed by different layers of protection such as solder mask, ENIG, or immersion silver, copper’s set up is the backbone to the PCB technology due to its efficiency and economic value.
Conclusion
To sum up, the application of gold, silver, copper in PCB demonstrates that these metals are vital for achieving the high levels of effectiveness, durability, and sustainability of electronic equipment. Gold is extremely conductive and has low corrosion properties; therefore, it is needed for applications where reliability and consistent connection are critical. Silver provides the best conductivity and is very useful where high frequency and or high speed are required for the signal transmission. Copper is the most utilized metal in PCBs owing to its fine blend of performance and cost, thus forming the basis of electronic circuits. In many ways, each metal meets requirements that are special to PCB design and production while pushing electronic technology forward.
Thus, the need for high performing and reliable electronics which the growing world of technology will continue to present a market for will remain. It is, therefore, clear that there is need to plan strategically if clients’ needs are to be met hence the need to consider the following: Despite this, the use of metals such as gold and silver among other precious metals, and the cheap nature of copper will continue to go a long way in satisfying such demands. Material science and development in manufacturing processes present improvements in the application those metals optimise the concept of PCB, and help in creating new innovative electronic components and products with better characteristics and reliability. Therefore, working with the peculiarities of gold, silver, and copper, the electronics industry will be able to expand and explore new possibilities of what is achievable in the sphere of modern electronics and their functions.