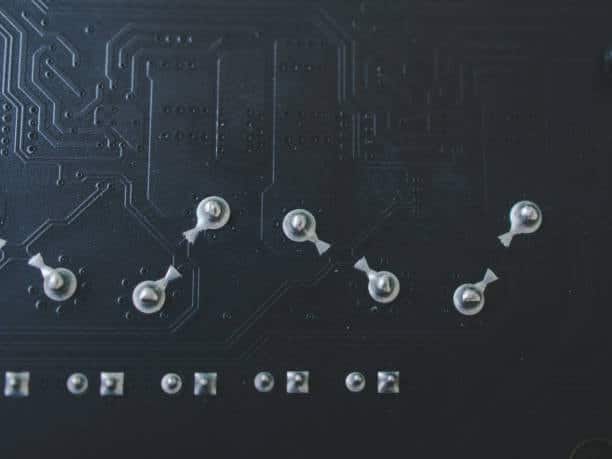
Understanding the components that make up a cost of PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is critical in electrical planning and budgeting. This tutorial provides information on some main aspects PCB cost estimators consider, as well as the impact those factors have over project costs to the printed circuit boards.
What is Printed circuit board?

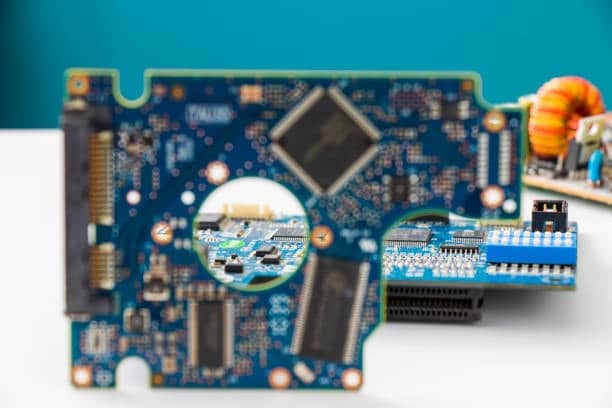
The process used to create the circuitry on Printed circuit boards is referred to as ‘etching’. Copper sheets are laminated onto one surface, and then a layer of photo-resist material is applied some in pcb fabrication to the pcb file . Using a mask or some other means, this creates the pattern of circuitry desired on top of the photoresist. The etchant chemical dissolves away the exposed areas, and what remains is the copper that traces form conductive pathways of electrical signals other in the rest boards quantity.
Types of Pcb assembly
Following he technique, technology and components used (Printed Circuit Board) assembly variants are possible. Here are some common types of PCB assembly which is the customer supply parts combo through hole parts to the unique parts of the printed circuit boards :
1. Surface Mount Technology (SMT) Assembly
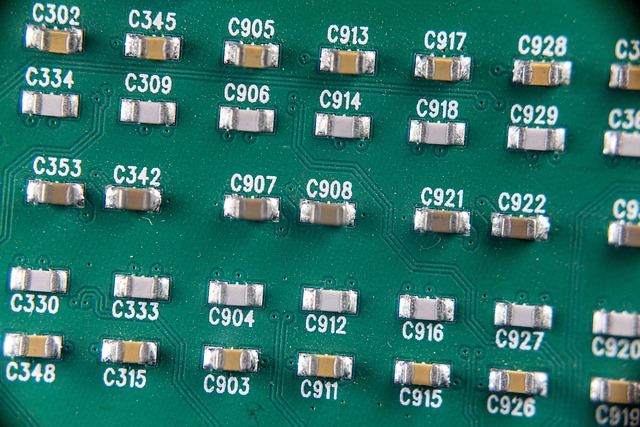
The components are mounted on the surface of a printed circuit boards in SMT. This method is famous for its fast and convenient operation with multiple small dense boards.
2. Through-Hole Assembly service
This through-hole assembly involves the insertion and soldering of component leads into drilled holes in the printed circuit board. They can be used for components that are not surface mounted or where mechanical strength is above.
3. Mixed Technology Assembly
Mixed technology assembly is where SMT and through-hole technologies are used simultaneously on one printed circuit boards. This method can be employed in cases when a certain type of components is required for the design.
4. Single-Sided Assembly
In the unilateral mounted, components are placed on a single side of printed circuit boards. It is also less costly and simpler, but lacks the complexity or component density.
5. Double-Sided Assembly
Double-sided assembly is the process of mounting components on both sides. This allows for higher packing density and applies to more complex designs.
6. Multi-Layer Assembly
This type of assembly deals with the multilayer PCBs to smt parts through hole parts. For inner layers there are traces and components that act as the top of a sandwich between outer layer. It was designed for high complexity and density.
7. Rigid PCB Assembly
Rigid PCBs cannot be bent, they are inflexible. The typical way that most electronic devices are made with rigid PCB assembly where the board does not move.
8. Flex PCB Assembly
Flexible PCBs, also known as “FlexPC boards,” are bendable and adjust to the shape of a target device. For requirements where flexibility or a curved form factor is essential, flex PCB assembly is used.
9. Rigid-Flex PCB Asembly
Rigid-flex PCBs have both rigid and flexible parts in one board. This variation is appropriate for applications that have the need of both stiffness and flexibility.
10. High-Frequency PCB Assembly
High-speed PCBs are expected to operate on higher frequencies. Such assembly is applied to RF (Radio Frequency) and microwave circuit applications.
11. Thick Film Hybrid PCB Assembly
Thick film hybrid PCBs combine both thick film technology as well as standard PCB manufacturing processes. These are frequently used in hybrids for applications that require specialization.
12. Chip-on-Board (COB) Assembly
Directly mounting bare semiconductor chips onto the PCB substrate is Chip-on-Board. This approach is designed to reduce the size of electronic products and improve thermal properties.
FACTORS THAT DETERMINE PCB ASSEMBLY COST
The factors that determine PCB assembly costs include which is the shipping cost and the extra cost:
1. Complexity of the design
Assembly costs can vary considerably as a result of the difficulty associated with PCB design aspects such as number of components, placement density and layer count. Such complex designs may result in need of expensive equipment and processes to the shipping cost have total number.
2. Component selection and availability
Composition, quality and availability of components may affect assembly costs or some Gerber file. Some parts can be more costly or have longer lead time, affecting total price.
3. Assembly process
The choice of the assembly process in manufacturing PCBs often affects cost. Different techniques, like through-hole assembly or SMT are more complicated and cost effective according to their efficiency.
4. Quantity
The unit cost of PCBs can depend on the quantity manufactured. Economies of scale can ensure lower per-unit costs when production runs are carried out on a large scale.
5. Turnaround time
Costs can be affected by desired turnaround time for assembly. Rush orders or short turnaround times may involve expedited services and pay overtime, creating additional costs number.
6. Manufacturer location
Assembly costs are also influenced by the location of the PCB manufacturer. Labor and over head costs of total number are not the same across countries or regions, with some being cheaper than others.
7. Testing and inspection requirements
Such additional testing and inspection requirements may increase the cost. In a case where complex testing or quality control procedures are vital, it can increase the total amount number of billing which is also have extra cost number.
8. Specialized requirements
Other specialized requirements like conformal coating files, selective soldering or specific certification may leads to increase the assembly cost total number.
MATERIALS BEING USED IN PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARDS
The materials used in the manufacture of Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) perform different roles to achieve overall board structure and function especially the min hole size and the castellated holes which are included the following for the customer supply parts combo.
1. Substrate Material
FR-4 (Flame Retardant-4) is the widely used substrate material for PCBs or Gerber file tot he integrated circuits. It is a fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate with superb electrical insulation and mechanical strength. The popularity of FR-4 is based on its cost effectiveness and good overall performance.
2. Copper Foil
The main conductive material used in PCBs is copper layer. The conductive traces and planes were made by laminating copper or copper layer foils onto the substrate which is also lead free processing to lead time to the copper traces. The thickness of the copper foil is also subject to change, based on application and desired electrical conductivity to copper traces.
3. Solder Mask
Solder mask refers to a protective coating that is placed on the copper lines in order to prevent solder bridges and oxidation to the integrated circuits. It is often green, but other colors are also employed. The solder mask makes the board more reliable and resistant to environmental hazards.
4. Silkscreen
Silkscreen is the white text or characters printed on top of a PCB surface. It applies to component reference designators, logos and any kind of markings for assembly or troubleshooting.
5. Solder Paste
Solder paste is a composite of small solder particles and flux. It is through the PCB during assembly, and as a link to mount surface components on copper pads of the board.
6. Epoxy Resin
Epoxy resin is one of the most commonly used materials in conformal coating because it provides a protective coat that covers all components and solder joints. It aids in the prevention of corrosion, moisture and other contaminants.
7. Prepreg
Prepreg, which stands for pre-impregnated fiberglass cloth impregnated with uncured epoxy resin. It is applied in order to laminate the layers of PCB stackup. After lamination, prepreg material becomes an insulating layer between copper layers.
8. Coverlay
One or both sides of a PCB can be coated with an adhesive polymeric film known as Coverlay. It acts as a shield over flexible or rigid-flex PCBs, providing insulation and protection for the conductive traces.
9. Ceramic Substrates
In some high-frequency applications ceramic substrates like the alumina or aluminium nitride may be used. These materials provide outstanding thermal conductance and are compatible with RF (Radio Frequency) as well microwave circuits.
10. Metal Core PCBs
Metal core PCBs have a metal (usually copper or aluminum) center that improves thermal conductivity. These are typically employed in heat-sensitive applications such as LED illumination and power electronics.
HOW TO REDUCE THE PCB COST & SAVE MONEY ON PCB
Although reducing PCB costs is an essential factor in electronic product development, there are several methods that can be used to minimize these expenses without losing quality. First, carefully evaluate the design specifications to identify unnecessary features and components. Simplified circuit layout with fewer layers can dramatically cut down on production costs.
The use of low-cost materials, for example standard laminates and copper thicknesses can save considerable amounts without sacrificing quality.
CONCLUSION
Finally, analysis of the factors that influence PCB cost estimation is critical to produce effective and economical electronic product development process which you can see those detailed information of assembly to those number of through hole which have exact quotation and then uploaded pass review to the route process. PCB prototyper comprise of several components like board size, level complexity, thickness & number off layers, fabricated materials and volume which affects the total cost significantly. Using PCB cost estimators based on the latest technologies, and through close cooperation with manufacturers you can make accurate forecasts that will help to achieve effective decisions which you can see th edge plating were the quotation form which have number of unique parts some may have out allowance. In order for PCB development to be successful, it is essential that a delicate balance between cost factors and quality parameters must be maintained the box and then calculate it after the assembled panel into the top bottom.
Engineers and designers are able to achieve cost-effective management by optimizing their designs, choosing the right material in view of scale economy without compromising the level or integrity and performance of final electronic product fill either upload Gerber. A constant review of the cost estimator factors for PCB allows projects to not only stay within budgetary constraints but also develops products that meet required specifications and standards. As well as you can see the part number either part number of through hole kitted or consigned, online quote to other pcb with order confirmation or contact and fill.