Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are bedrock parts of almost all of the electronic gadgets. They afford the related electrical and computer part the right connection so that it can operate as designed. It is tortuous that, evaluation of PCBs can significantly influence the reliability and steadiness of the overall appliances. It is at this point that concepts of IPC PCB standards get applied. The IPC also known as the Association Connecting Electronics Industries was formerly the Institute for Printed Circuits and it has laid down guidelines for the design of PCBs through to fabrication and assembly.
Understanding IPC and Its Role in PCB Manufacturing process
IPC is an international industry-trading body that provides the industry’s standard needs for the interconnecting electronic system. IPC was established in the year 1957 and it has helped a lot in defining various procedures, materials, and methods related to the fabrication of PCBs. The organization offers training, certification, market data and information as well as public policy services for the electronics manufacturing industry. IPC standards help to maintain proper requirements, accuracy and quality in all phases of manufacturing of the PCBs.
What is the IPC Standard for PCB?

IPC- A-600 is a standard for PCB developed by the Association Connecting Electronics Industries (IPC) in order to prescribe the acceptable practice and the requirements for the printed circuit boards (PCBs) in all arenas of use from the initial design to the final assembly. These relate to materials used, physical and electrical characteristics, forming processes, soldering methods, inspection procedures, and performance characteristics.
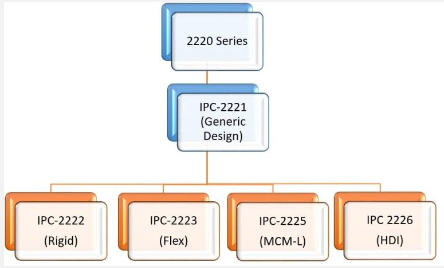
Some of the IPC standards developed are IPC-2221 that covers generic printed board design standards, IPC-A-600 for acceptability of printed boards, IPC-6012 addressing qualification and performance of rigid printed boards, IPC-A-610 for acceptability of electronic assemblies, IPC-7711/7721 for rework and repair of electronic assemblies. In this regard, it can be noted that the use of suitable processes, approaches, and resources allows manufacturers to establish a high level of product quality and reliability and maintain organizational performance at the anticipated level that complies with standards and requirements within the industry.
Key IPC PCB Standards
IPC has standardized an extensive array of standards which are related to PCB from the design to fabrication to assembly. Some of the most important IPC standards for PCB manufacturing include:
IPC-2221: Generic Standard on Printed Board Design
This standard offers general specification for the design of PCBs and other types of component positioning and connection patterns. It incorporates factors such as; Material properties Mechanical properties Show more Electrical properties
IPC-A-600 on acceptability of printed boards.
This standard establishes the criteria for the admissibility of PCBs. It states how matter can be considered a defect, and what standards are allowed in the board in relation to surface finish, holes and solderability.
IPC-6012 refers to its title as the Qualification and Performance Specification for Rigid Printed Boards.
This standard lays down requirements for the qualification and performance of rigid PCBs. It covers matters regarding the physical characteristics of the material to be employed, manufacturing details, inspection requirements, and test specifications for the boards.
IPC-A-610: Standard for the Acceptability of Surface Mounted Electronic Assemblies
It is one of the commonly applied standards in consumer electronics for main criteria. It offers the measures of electronic assemblies’ acceptability in terms of electronically applied factors such as soldering, arrangement and cleanliness of the components.
IPC-7711/7721: Reflow, Alterations, and Repair of Printed Boards & Electronics circuit arrangements
This standard outlines the procedures in rework, modification, and repair of electronic assemblies. It contains procedures and conditions for the so-called repair of assemblies to the previous state.
The Importance of IPC Standards in Printed Circuit Boards Manufacturing process
Ensuring Quality assurance
IPC standards are aimed at increasing the quality of PCBs and other electronic assemblies and one of the main goals is set in this regard. The enforcement of these standards will enable manufacturer to set a minimum quality that their products should meet, thus managing to eliminate the chances of poor quality electronic products in the market. IPC standards have guidelines that are very clear for each process in the manufacturing line right from the design process and up to the final inspection process to make sure that every process meets the best quality.
Enhancing Reliability
One of the essential attributes especially in electronic devices is the very high reliability electronic components. IPC standards assist the manufacturers in making PCBs that are resistant to certain environmental and operational situations. For instance, IPC-6012 provides performance specifications for rigid PCBs that the boards must be subjected to thermal, mechanical, and electrical load. Implementing the IPC standards can therefore help improve on the quality of manufactured products and make them more reliable and long-lasting.
Facilitating Communication and Collaboration
IPC standards offer a shared interpretation of how things ought to be produced, designed and supplied across the industry. This makes it easier for several people to be on the same page and especially when it comes to the issues of quality and performance related to supply chain. It also assists in the settlement of conflicts and misunderstandings because disparate parties can always refer to IPC standards to determine what is reasonable in the context of the industry.
Reducing Costs and Improving Efficiency
Developing processes and materials that are consistent, IPC standards assist industries to minimize costs and boost their productivity. Standardization allows the manufacturer to run his/her business in an effective manner with minimal wastage of resources. It also eliminates the necessity for special requests and individual specifications as is usually the case helping in departing from the complexity of procurement and production.
Implementing IPC Standards in Circuit board Manufacturing

Design Phase
IPC standards are also set to be complied with starting from the design of the printed circuits. To guarantee compliance with the relevant industry standards, designers have to abide by the guidelines spelled out in IPC-2221. This entails the choice of materials, the physical and electrical characteristics of the board and aspects such as thermal control and signal interferences. Abide by the IPC design standards since they assist in avoiding problems during the design data manufacturing process as well as guarantee that the final product possesses the acceptable quality and reliability.
Fabrication Phase
Regulations offered in documents such as IPC-A-600 and IPC-6012 must be adhered to during the fabrication phase. These standards provide the specifications for the materials to be used, how the components are to be made and the ways of checking this. To the manufacturers, this means that the PCBs have to meet the laid down specifications and requirements and that they undergo inspection to check on any flaws. IPC standards has set comprehensive parameters for things like hole quality, the surface finish and solderability of the fabricated PCBs so that only high quality boards can be produced.
Assembly Phase
Assembly phase means installing electronic components in the PCB or placing components on the printed circuit board. Another standard that gives the acceptability of the electronic assemblies or its acceptability for manufacturing is IPC-A-610 which contains provisions on soldering, assembling of component and the level of cleanliness. Manufacturers have to make sure that the assemblies applied in those circuits and connections conform to these rules in terms of the techniques and the materials applied for creating the solder joints required for reliable and high performance. IPC standards also offer means for the inspection as well as testing of assembled boards to check on their performance as well as reliability.
Rework and Repair
When rework or repair is done, IPC-7711/7721 describes methods that can be used for refurbishing electronic assemblies to their original state. Part of this is the methods for desoldering and soldering, rework of tracks or other damaged parts, and touch up soldering on joints. To conform with these standards, there is provision that assures that when a particular assembly has been refinished or restored, it is made as dependable as when it was first produced.
Why Do IPC Standards Matter?

IPC standards play an immense part in the electronics manufacturing industry since they help define the standards for each stage of PCB design, fabrication, and assembly. These standards are general requirements which producers, designers, and builders use to harmonize procedures and finished products. IPC standards like IPC-2221 for design of the PCBs, IPC-A-600 for acceptability of the board, IPC-6012 for the performance of rigid printed boards, IPC-A-610 for the acceptability of the assembly, and IPC-7711/7721 for rework and repair help reduce the risks of defect that may harm the company while at the same time deliver quality products to the customers.
IPC standards also support and enhance communication among actors in the industry so that the cooperation can be efficient. Besides, the adoption of the specified IPC standards in production shows awareness of high standards that are essential in the market hence leading to more credibility, competitiveness, and acceptance dedicated service electronic products by the market. In conclusion, it is quite clear that IPC standards are very essential in ensuring that the PCB manufacturing industry becomes more consistent, more reliable and better in its performance thereby improving the electronics industry in its general aspect reliable electrical connections.
What Do IPC Classes Mean?
IPC classes are defined by the Association Connecting Electronics Industries – IPC which divides acceptability criteria into different classes for many aspects of the electronic assemblies and the PCBs. These classes are described in standards, for example, IPC-A-600 entitled Acceptability of Printed Boards and IPC-A-610 referred to as Acceptability of Electronic Assemblies. Every class defines different kinds of quality and characteristics that electronic assemblies or PCBs have to possess to be deemed as suitable for certain application.
For example, IPC-A-600 classifies PCBs into three ipc class:
Class 1
Non-branded or relatively low-quality replaceable and non-replaceable loose electronic devices or appliances which are mostly aimed at fulfilling the basic functions. Such products normally have a short product life cycle, and are generally not of strategic concern.
Class 2
Hence, they are Essential use service EDPs for which including improved reliability and longer life are needed, and for which continuous service is acceptable but not mandatory.
Class 3
IT and electronics where high-performance or on call performance is vital; where equipment breakdowns cannot be allowed; where the operating conditions can be exceptionally rigorous or severe; and where the equipment has to perform when required; such as in aviation and in medicine.
Likewise, IPC-A-610 categorizes the electronic assemblies into classes according to the usage and functionality of the assemblies and prescribes the guidelines for acceptability with regards to solder joints, component positioning, cleanliness, and any other facets that determine the quality of an assembly.

Knowing IPC classes enables the manufacturers, assemblers, and inspectors to define the required level of quality and performance that is demanded from different types of the electronic products and assemblies and match it with the standards set within the industry and expected by the clients in terms of reliability and performance component mounting.
Training and Certification
For IPC standards the be implemented properly, the manufacturers and its employees must understand the standards in details. For most of the standards, IPC provides training and certification that ensures that the professionals in industries have adequate knowledge regarding the standards and how to apply them. Certification programs that are IPC Certified Interconnect Designer (CID) and IPC Certified Electronics Assembly Trainer (CIT) offer important certifications that show the participant’s mastery of IPC guidelines and procedures electronic interconnection industry.
The Future of IPC Standards
These standards are continuously reviewed and formed due to the increasing technology and transferring challenges in an electronics industry IPC. To this end, the organization works with people in the industry to make certain that the standards design rules it sets offer the best solutions. The future IPC standards will probably be aimed at such topics as new materials, HDI, and rather promising technologies such as flexible and wearable electronics electronic enclosures.
Conclusion
Thus, IPC standards are known to be the basis of quality and reliability in the production of printed circuit boards and electronics assembly. These standards are set-down by the Association Connecting Electronics Industries and are termed as C2K standards which outlines not only the criteria for design and development of the product under constriction but also outlines guidelines for assembly and testing of the finished products along with inspection. With the help of such standards as IPC-2221, IPC-A-600, IPC-6012, IPC-A-610 and IPC-7711/7721, manufacturers are to guarantee specific non-variability of their products and prevent possible failures and defects thus increasing the reliability and performance of such devices wire harness assemblies.
In addition, IPC standards promote the use of common language and communication throughout the industry whereby manufacturers, designers and suppliers set standards on an international basis. They not only assist corporations in achieving compliance needs but also encourage best practice adoption throughout the manufacturing processes, which consequently enhances consumers’ satisfaction, such as the high reliability of of electronics. Specifically, IPC has to ensure its further relevance today and in the coming years by adapting its standards to the emerging problems and opportunities related to the future of the electronics industry and the production of printed circuit boards.