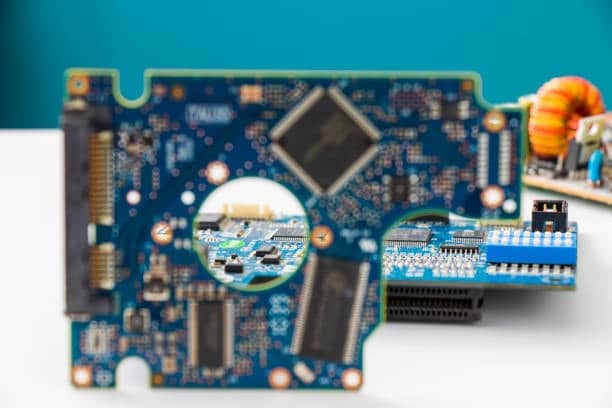
The Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is the backbone of modern electronics, being the underpinning of an extensive range of electric devices we all use nowadays. One important element of the PCB is the laminate material, which gives both the structural stability and the electrical insulation required for its function. A comprehensive knowledge of PCB laminate material types should be in mind to make good design of reliable and superior electronic circuits. Here, we will be diving into some of the most important PCB laminates you need to be aware of.
What is Laminate in PCB?

In PCBCs, laminate materials is the basic material that makes up the substrate where all the components and circuits are laid down. It becomes composite material and, thereby, is the structure of several layers that provides a support as well as an insulation for electrical components. The dielectric constant is quite a relevant parameter, for it allows determining how perfectly the material shields against electrical signals. Thermal conductivity is another significant factor which determines the degree of success of thermal dissipation from a motherboard. Besides, while many of them are open to fire protection, this is primarily of great importance from safety point of view. Warping mitigation is also a fundamental aspect of the construction that guarantees that the boardwill maintain its flatness throughout the usage period. It is therefore a crucial one since it defines the performance and reliability of the PCB.
What are the types of printed circuit board material?
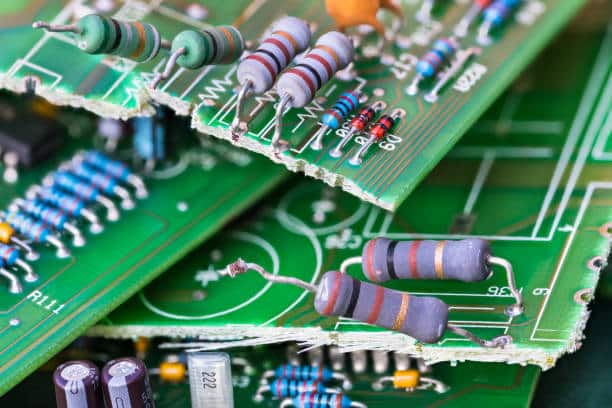

There are different laminate materials types of materials used in printed circuit boards (PCBs), each with its own characteristics and applications:

FR-4
FEP is the most commonly used and has a very low loss tangent. It is a fiberglass-epoxy lamination that comprises of superior electrical insulation and acceptable mechanical strength (high tg epoxy laminate) or in woven glass. The FR-4 is one of de most known materials because of its affordability and versatility that have made it suitable for many kinds of applications.
FR-1 and FR-2
These Types of boards are similar to FR-4 but instead made from paper or fiberglass which had phenolic resin when its impregnated. They are the forerunner in the FR-4 replacement industry and provide weaker mechanical properties strength, flame rating or flame resistant, hence less expensive.
Metal Core Materials
The materials being used are called MCPCBs which have a metal core, mostly aluminum or copper clad laminate pcb, that enables high thermal conductivity such as thermal expansion, thermal performance, thermal properties. Fans are integral part in PCBs where the aspect of heat dissipation is resistance to electronics. Akin to this, they are used in LED lighting and power electronics.
Polyimide laminates
It is a highly stable and chemically resistant laminate material due to its thermal stability and top temperature of 200℃. It is particularly important for flexible PCBs, for which it is a commonly used material, and the applications, where temperature is a critical factor When working with multilayer PCBs, rigid-flex circuit boards , or high-density flexible circuit boards.
Rogers Corporation Materials
The company is a renowned manufacturing facility that provides various top notch laminate products specially lint skeleton for radio frequency and microwave applications. These composites demonstrate features as low dielectric loss and outstanding torsion resistance at high frequencies.
Teflon (PTFE)
PTFE belongs to a class of plotted films, which is commonly used for its outstanding electric performance, i.e. low dielectric constant and low loss tangent. It is a notable down the line application in high frequency.
What is the importance of pcb laminate material?
The selection of PCB laminate material is a vital issue that can have significant consequences for the performance, dependability and the cost of the printed circuit board which you can see pcb laminate material’s ability PCB laminate materials should have a moisture absorption rate of between 0.01% and 0.2%.. For instance, properties like electrical insulation, mechanical support, thermal management, flame retardancy and dimensional stability are some of the features which contribute significantly towards the unadulterated functionality of the PCBs.

The conclusion part is that the choice of the PCB laminate material is a very significant stage of the PCB design process. One has to look into different bits, such as the electric, mechanical, thermal, and the price related of the material to guarantee that the PCB can satisfy its user and prove to be of good reliability over the whole time of the service.
What is copper clad laminate?
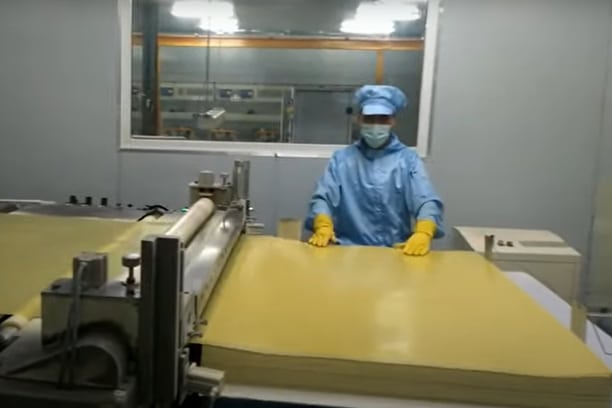

Copper clad laminate pcb which is abbreviated as CCL is a variety of material specially designed for printed circuit boards (PCBs) fabrications. It is composed of a thin layer of copper sheet (foil) sprayed onto a substrate material, as a rule made of woven fiberglass with epoxy resin or glass reinforced epoxy laminate copper weights . The literal substance of the PCB acts as the foundation for the building of a high frequency circuits while the copper foil or copper traces is used to produce the circuitry. Copper clad laminate is essential for PCBs because it floods the need of the concerned electricity to circulate through the board and gives good mechanical strength and thermal stability at the same time of the copper clad laminates.
What are those properties for pcb materials for consideration?
The materials are a crucial factor when choosing the PCB properties as it can determine whether the board will be able to fulfill the high temperature applications -based requirements. Here are some key properties to consider:
Dielectric Constant
This property requires electromagnetic waves to cross the metal’s boundary surface, dissipating a certain amount of transmitted power in the process by using dielectric materials. While the one having low dielectric constant is preferable for those at high frequencies laminate materials, to reduce signal loss.
Thermal Conductivity
In this field, the subtlety of heat transfer is important because of the components heat emittance. High conductivity helps the machinery to remain cool.
Flame Retardancy
Flame retardancy is a common feature in demanded applications for PCB’s as a rule of safety. Since fire safety compliance standards have to be met, the materials should be duly compliant.
Mechanical Strength
The plate shall be of a suitable strength to function as a support to the components and withstanding loads during a mechanical operation and the assembly process.
Dimensional Stability
The material is needed to have dimensions that are stable within the given temperature and environmental conditions range for the entire life for the electronic components.
Chemical Resistance
The material should be able to withstand chemical compounds and solvents in the processes of manufacturing and operation in order to prevent any damage from occurring.
Cost
The cost of the material is a key factor, or even the cost-in-matter, especially for high-demanding applications.
Environmental Considerations
An example is that the devices which spare the environment from some harmful materials and comply with the directive of RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) extreme environmental stability.
Printed Circuits Material Suppliers
Here are some key printed circuit board (PCB) material suppliers. Here are some key printed circuit board (PCB) material suppliers:
These partners are reputable global suppliers of well-known quality materials that are highly sought after by PCB designers or manufacturers.
High-speed networks drive pcb laminate and material choices
Designing a high-speed network necessitates the selection of PCBs made of specific laminates and material for the optimal performance criterion. Here’s how high-speed networks drive these choices:
Signal Integrity
The integrity of high-speed signals decays over some distance due to the possible obstruction from impedance mismatch, signal reflections, chromatic dispersion, etc. Electronic PCB laminates artificing in the form of discontinuous RF signal propagation due to controlled dielectric constants and low loss tangent contribute to the signal integrity maintenance.
Frequency Considerations
High-speed network operate on a higher range of frequencies which necessitate the use of low lossy and narrow band PCB electronic material fluctuation over a wide frequency range. Substrates which are made from these high-frequency laminates and PTFE-based materials are most often utilized because of the fact that they have the best properties for use at a higher frequency.
Thermal Management
The heat in the network becomes higher due to the amount of light in some points where processors and switches are located. PCB material which is very good for heat conductibility helps dissipating heat allowed and this prevents network overheating problems which maintains network reliability.
Mechanical Stability
High-speed networks may fail due to the strain of clicking them in or out of the device In case of PCB laminates with high strain regimes and dimensional stability is a primary parameter to assure the board does not suffer the signal irregularity under such condition.
Material Cost
Proper performance is important, but cost issues have their much-needed share of the pie, too. On the argument of cost-effectiveness combined with the fast running network applications often requires highly advanced materials, but in most cases the required performance standards are left unattended.
Without a doubt, high-speed networks push for PCB laminate and material selection through requirement for materials that give out best quality signal integrity, full electrical integrity, efficient thermal management, and mechanical stability, but in a limited price range.
FAQS
The released matter from the print circuit laminate materials comes across as another problem.
How is it possible that material data sheets are different from dielectric constants on the same circuit boards?
The data sheets which show the breakdown of dielectric constants are simply intended to cater to the needs of a specific market segment and are not specific materials only. A laminate is something that has four exactly distinct layers. We may get different dielectric constant values even when layers are all up and running.
Is it possible to do a higher layer count by using only materials of high frequency?
The dynamic, encounters which are hence possible and sometimes even needed are imaginable. Victorian writers explore common themes such as social class, gender roles, industrialization, environmental degradation, and individual morality in their poems, short stories, and novels. Through these works, they express their views and perspectives on societal issues. Whether the digital signal is significant or not, what kind of requirements it needs to accommodate is just something that you have to determine yourself.
Can high-frequency materials v-score?
The automatic response is that it is not. Along with the glossy high-frequency laminate materials, these properties are soft and fibrous. If you installed two circular saws on the side by side, they will create a “V” shape. If you use those tools on a fragile surface, you will be surprised that they are so weak to cut through that surface or in higher glass transition temperatures or high frequency circuits.
What are the common types of PCB laminate materials?
Two of the most popular laminate materials used in PCBs include the FR-4, FR-1, and FR-2, polyimide, Rogers Corporation, metal core, ceramic materials, and Teflon materials (PTFE) to the manufacturing Teflon pcbs.
What are the key properties to consider when selecting a PCB laminate material?
It is advisable to look for the following aspects: dielectric constant, thermoconductivity, fire retardancy, mechanical strength, dimensional stability and affordable price
How does the choice of PCB laminate material impact the performance of a printed circuit board?
The variation of PCB laminate material material can connect to electrical performance, thermal and mechanical performance of printed circuit board indirectly. It inches to signal integrity, thermal management, reliability, and cost. Materials Coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) 370 HR X 13 ppm/°C Y 14 ppm/°C Z 45 ppm/°C Rogers 4350B X 10 ppm/°C Y 12 ppm/°C Z 32 ppm/°C As a material’s temperature rises past Tg, the CTE will rise as well.
What are the best practices for selecting a PCB laminate material?
Optimizer methods should start with understanding of the demands on the coating; inspecting the excellent electrical properties and mechanical characteristics of the material; assessing the cost and availability and finishing up with testing in the specifying environment.
How can I ensure the PCB laminate material I choose meets the requirements of my application?
By means of comprehensive evaluation of properties of the laminate material, testing applications in different conditions, and engaging experts or providers in the PCB industry, you can be very confident that the material will meet your project’s requirements.
What is an impedance-controlled stack-up?
To enhance the uniformity of characteristic impedance throughout the PCB, the impedance-controlled stack- up is introduced. This is significant in high-speed digital and RF applications as the reliability of a system depends on impedance matching. Any mismatches can lead to signal attenuation and noise. A stack up with controlled impedance may be made of various laminate types having a particular dielectric constant and thickness that result in the specified characteristic impedance.
The material data sheets exhibit varied permittivity values within the identical board. How is such discrepancy feasible?
After reviewing a data sheet, the specified dielectric constants apply to a broad material spectrum, not only some isolated areas. When this laminate is viewed from the surface we may encounter a possible composite of four layers in a laminate. Comprising the same stackup still the arrays of dielectric constants could be different for separate dielectric layers.
Can construct multi-layer circuits with a higher layer count using only high-frequency materials in basic stack-ups?
Yes, it is possible to construct multi-layer circuits with a higher layer count using only high-frequency materials in basic stack-ups. In that sense, there are many points that should be taken into account. For signal propagation with high-frequency materials, the dielectric constant is frequently low, which sometime affects the impedance rate. While it is necessary to confirm the dielectric constants of the high-frequency materials in different layers such as the microwave band, the millimeter-wave band and others, those dielectric constants must also be well-matched to prevent the formation of signal integrity problems for decomposition temperature. Apart from that, the ruling materials of high-frequency are usually more expensive relative to unique FR-4 materials, which might increase the final costs through the Printed Circuit Boards. Among other factors to be considered may be this matter of availability of high-frequency materials, as they may not be as yet easily accessible as usual materials to the pcb manufacturing process. Taking into account high-frequency substrates for multilayer boards with a higher layer near is not really a complicating matter. However, the problem might be in the other direction, that is the abundance of these factors. Thus, it is necessary to balance those aspects in order to have the best performance and cost-effective technology for your specific application.
Pcb laminate vs prepreg
PCB laminate and prepreg, as well as the other components used, are vital materials that come together to create the printed circuit boards (PCBs). PCB laminate fulfill technical functions of the PCB; they are mechanical supports and insulators. It is often, constructed from glass fiber ( or higher glass transition temperature) that is reinforced with epoxy resin and is known among the experts as FR-4. This material is commonly implemented in the inner layers of the CPU or in glass fiber reinforcement. On the contrary, prepregs are made of a cloth of fiberglass and wrapped up with an uncured epoxy resin glass transition temperature tg. It is responsible for the bonding of the layers while manufacturing the PCB through the conduction of lamination process. Prepreg can be placed between layers of copper foil and two copper PCBs join together after they have been exposed to heat and pressure, curing the resin and forming a solid bond to create a multi-layered PCB. Primitive circuit boards have their structure base material on the laminate, while in turn, prepreg is a gluing material that builds edge plane boards.
What are the advantages of utilizing high-frequency laminate materials in PCB design?
The proper application of conductive substrate laminate or high-frequency laminate materials in PCB designing provides numerous benefits. Low tangent dielectric constants and loss tangents of these materials are what differentiates them from the most common PCB materials – FR-4 and makes them the best candidate for high-frequency application. Furthermore, they give superior dimensional stability which makes it possible for the opposing impedance to be controlled precisely and the signal integrity in consequence is maintained. Moreover this, high-frequency laminates possess superior thermal properties features that enable the cooling of the circuitry in high-power operations. Consequently, all these materials are powerful and are now being used to create PCBs with exceptional working frequencies.
What are the primary similarities between an FR4 type and the IPC specification?
FR4 and this IPC standard share a piece of common ground which is that both of them prescribe the material to be used in a base material of PCBs (printed circuit board). FR4 is a versatile grade of fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate or bt epoxy laminate that is used in applications where fire and electrical considerations are other priorities. However, the IPC specification is more of a guide, as it establishes design, manufacturing printed circuit boards, and test standards, with the inclusion of FR4 as a material of choice either in the fabricate printed circuit boards or producing printed circuit boards . FR4 and IPC specifications are just necessary because they stipulate the proper quality and performance of PCBs, which in turn are trusted and suitable for a structural range of applications.