What is Stencil in PCB Manufacturing? An Essential Guide for Beginners
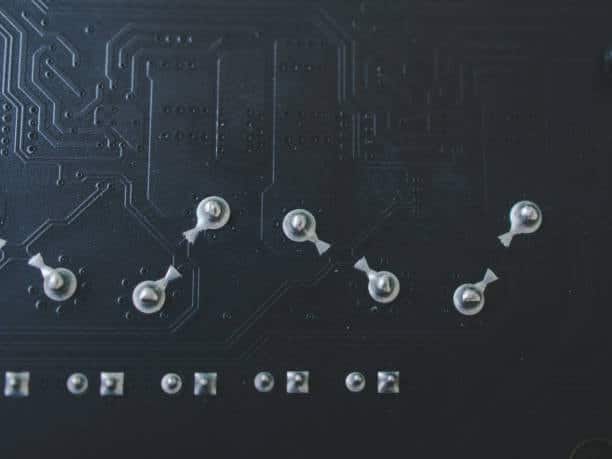
In PCB manufacturing, stencils are very important tools that are used in the dispensing of solder paste onto the printed circuit boards. This guide educates the reader about the definition of PCB stencils, categories of stencils, materials used for stencils, and how to conduct stencil creation as well as stencil’s utilization for the assembly of PCBs. Getting to know about stencils is important because it helps new users achieve the right quality and effectiveness of printed circuit boards.
Demystifying IPC PCB Standards: Ensuring Quality and Reliability in PCB Manufacturing
Thus, IPC standards occupy a special position in electronics manufacturing playing vital importance by offering detailed and complete information on the design, fabrication, and assembly of PCBs. It is critical to implement key standards like IPC-2221 that assist in the outcome of more reliable design methods in addition to IPC-A-600 and IPC-6012 that aims to outline board acceptability and performance requirements. IPC-A-610 provide standards for acceptable assembly techniques and IPC-7711/7721 outlines the rework and repair procedures. These standards divide products into classes according to the application needs which will guarantee electronic assemblies specific levels of performances and reliability.
When manufacturers adhere to the International Production Competitiveness standards they are not only able to produce quality electronic products, but they are also able to do so more efficiently hence cutting down the costs incurred in production and increasing on the ease of trade since there are standard measures that are taken into account when determining the acceptability of products in the international market pcb manufacturer. The continuous development and update on the standards being set by IPC instill growth and development in the electronics industries as it also adapts to the new technologies in the market. When following the guidelines set by IPC, manufacturers can be certain that they are maintaining the highest standards in the global electronics industry, gain customers’ trust, and guide the improvements of the electronics manufacturing processes.
Silver Circuit Board: Unlocking Superior Performance and Reliability in Modern Electronics
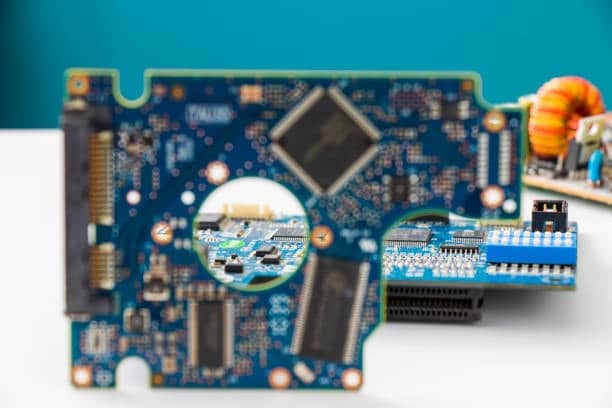

Most people are familiar with copper printed circuit boards, but it is essential to know that they have their counterparts in silver printed circuit board with better conductivity, performance, and durability. This post describes silver in circuit boards, where its helpful, and possible uses are gently explaining the cause behind the preference for this precious metal used across high-function electronic products. This paper will also explore the actual manufacturing process of this type of circuit board, how it is different from the conventional copper circuit boards, what can be expected in the future concerning types of silver circuit boards and new development that may be in the offing.
How to Prevent Solder Non-Wetting in Your Electronics Projects

The document titled “How to Prevent Solder Non-Wetting in Your Electronics Projects” provides a comprehensive overview of non-wetting phenomena in soldering, a common defect in electronics manufacturing where molten solder fails to properly adhere and spread over the metal surfaces being soldered. Non-wetting results in weak or incomplete joints that can compromise the integrity and functionality of electronic assemblies. The article explores the causes of non-wetting, such as surface contamination, improper flux activity, incorrect soldering temperatures, and incompatible materials. It emphasizes the importance of proper surface preparation, flux selection, and temperature control to prevent these defects. Techniques and tips are provided to help practitioners achieve strong and reliable soldered joints, thereby improving the overall quality and durability of electronic products.
The Ultimate Guide to Understanding what is flux for soldering
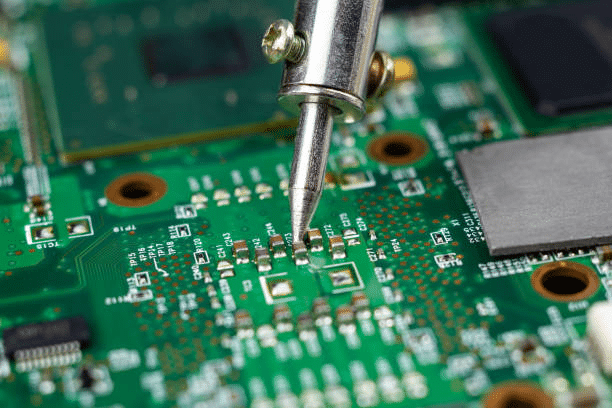
The document titled “The Ultimate Guide to Understanding What is Flux for Soldering” explains the crucial role of flux in the soldering process. Flux is a chemical agent used to promote the clean and efficient flow of solder by removing oxides and other impurities from metal surfaces during soldering, which facilitates better wetting and bonding of the solder to the metals. The guide outlines various types of flux, including rosin, water-soluble, no-clean, and organic acid fluxes, each suited to different soldering requirements and conditions. Flux not only cleans metal surfaces but also protects them from oxidation during soldering, enhances thermal conductivity, and helps manage heat transfer, making it indispensable for creating strong, reliable electronic connections. The document also describes the typical process of applying flux in soldering operations, emphasizing its importance in achieving high-quality solder joints in electronic manufacturing.
Unlocking the Secrets of PCB Drill Size: A Comprehensive Guide for Designers
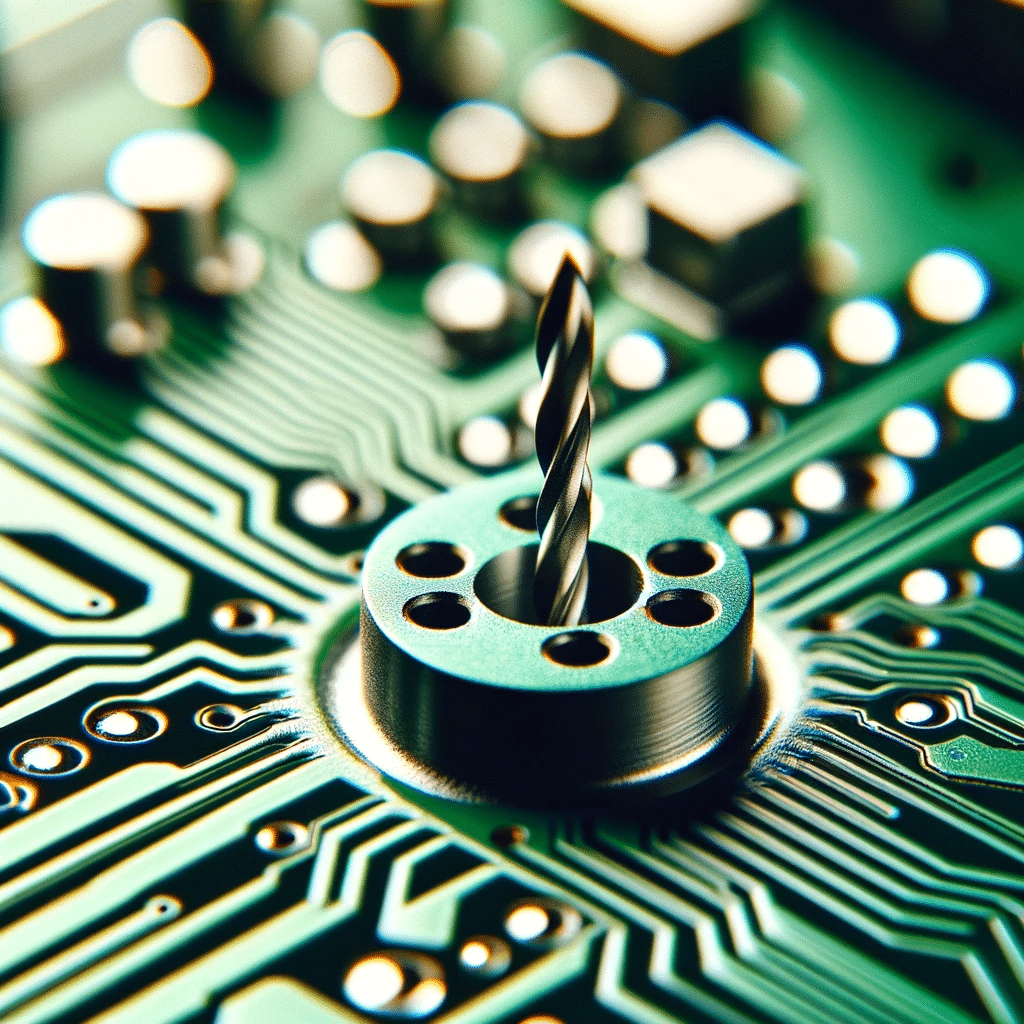
The document titled “Unlocking the Secrets of PCB Drill Size: A Comprehensive Guide for Designers” provides an in-depth analysis of the critical role of drill sizes in PCB manufacturing and their impact on the functionality and reliability of printed circuit boards. It explains that selecting the correct drill size is essential for component alignment, optimal conductivity, and preventing circuit failures. The guide discusses various standard drill sizes used in PCB production, their corresponding hole diameters, and the factors that influence drill size selection, including technological advances and manufacturing capabilities. Additionally, the document highlights the importance of precision in drilling to accommodate high component densities and complex designs, emphasizing the need for ongoing collaboration with PCB manufacturers to ensure the drill sizes meet specific design requirements. This guide serves as a valuable resource for PCB designers, helping them understand and apply the right drill sizes to improve product quality and performance.
Demystifying Standard FR4 Thickness: A Comprehensive Guide for PCB Designers
The document titled “Demystifying Standard FR4 Thickness: In the article titled “A Comprehensive Guide for PCB Designers”, the author details extensively the FRR material, popular among PCBs fabricators for its good electrical insulation and mechanical strength properties. It states not only the different wavelengths of FR4 but how they are applied to PCB designs and functions. FR4 with a thickness standard of 1.57 on PCBs is common; however, it may vary for specific design requirements in proportion to 0.78 and 2.36. Selecting the FR4 thickness impacts many PCB design aspects, mostly those related to the mechanical strength, thermal resistance and the electrical characteristics. This tutorial will become a helpful toolbox for PC board designers where they can find a reasoned solution for a material thickness to attain better shot of their product functions and durability. It further talks on the recent achievements in FR4 technology, which include improvements of thermal conductivity and the introduction of 2 types of fiberglass cloth and epoxy resins used by FR4, which expands the product range and also enhance the printed circuit boards performance on FR4.
The Ultimate Guide to Solder Paste: Everything You Need to Know

The document titled “The Ultimate Guide to Solder Paste: Everything You Need to Know” offers an extensive exploration of solder paste, emphasizing its crucial role in electronics manufacturing, particularly in ensuring the quality and reliability of electronic components. It details the composition of solder paste, which typically includes a blend of alloy and flux, aiding in effective solder bonding by removing oxides and improving wetting. The guide discusses different types of solder paste, such as lead-based and lead-free options, and outlines their applications in surface mount technology (SMT). Techniques like stencil printing and syringe dispensing are explained as methods for applying solder paste to printed circuit boards (PCBs). Additionally, the document covers storage recommendations to maintain solder paste’s efficacy and outlines its advantages, including precision in application and consistency in solder joints. This comprehensive overview provides essential knowledge for anyone involved in the electronic assembly process, highlighting solder paste’s indispensable role in modern manufacturing.
Mastering Bridge Solder Techniques: A Comprehensive Guide for Circuit Board Assembly
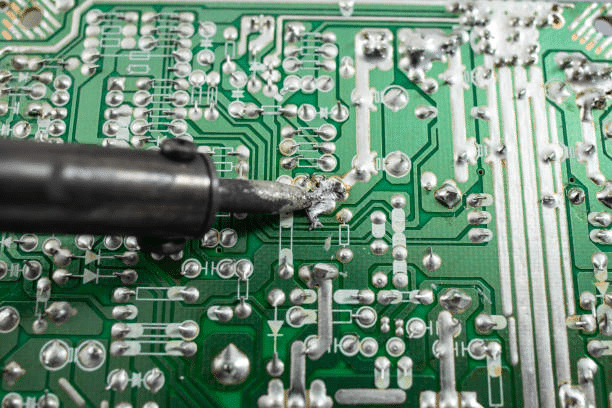
The document titled “Mastering Bridge Solder Techniques: “A Comprehensive Guide for Circuit Board Assembly and Assembly Errors” plays the main role for both electronics technicians and engineers who are trying to handle the issue of solder bridging electrical connections on the circuit board. Solder bridging phenomenon brings about when solder wastage forms a circuit line between two conductive elements causing device malfunction. thorough steps are outlined in the guide with a focus on the very essence of failed joints (solder bridges) prevention and, where applicable, resolving solder bridges by proper flux application, correct soldering iron temperature, and exact component placement. Technics of fixing solder bridges are deemed very vital in this skill training therefore emphasis is put on skills like using solder wick, desoldering pumps and fine-tip soldering irons to ensure that the soldering is done properly. At the same time, this document lists out corrective actions particularly for the common causes of the solder bridges and has the troubleshooting checklist to increase soldering precision and decrease future issue, so that the electronic assemblies could be quality-oriented and functional.
Mastering the Art of PCB Quick Turn: A Guide to Rapid Prototyping and Production
As the rapidly changing world of electronics design requires a short turn-around time for getting products from imagination to production line, quick-turn PCB design capability will provide a feasible solution to challenge the competition. This guide covers the threshold topics of prototyping and production very quickly, distinguishing between quick-turn services specialized for diverse projects that range from simple prototypes with basic to advanced technology to more complex flex and rigid-flex, prototyping, assembly, and turnkey solutions. The role of these services in this regard is not only to speed up product development but, in addition, to ensure that quality is maintained with shorter lead times. The ability of PCB Quick Turn for builders to cut greatly down on time-to-market is a plus, which, among other things, facilitates faster innovations and speedy reactions by way of market demands in quick turn pcb services.


