Various PCB finishing types should be known during building and manufacturing of printed circuit boards. Acquire informed knowledge about different PCB finishes each with its benefits and applications for better performance also the immersion tin finish and lead free finish press.
Designing and manufacturing processes of printed circuit boards require awareness of various types of PCB finishes. Get to know the different types of coatings on a printed circuit board (PCB), their respective advantages, and in what instances one would use each for the best yield.
What is surface finishes in PCB surface?
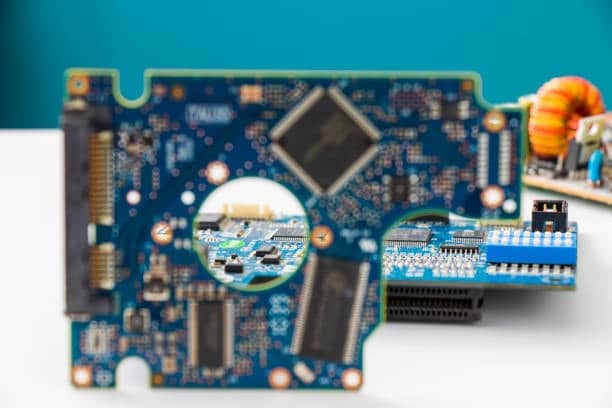
The surface finish of the PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is significant in determining how efficient, dependable and durable a device would be. The surface finish is almost a layer of coating on the copper traces exposed in PCB which are to protect them from oxidation, ease soldering and ensure better electrical conductivity. The following are some of the most common surface finishes in PCB manufacturing
1. HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling):
HASL is a traditional low-cost surface finish.
This process is defined by applying a layer of molten solder onto PCB after which hot air levels the melted and removed any excess that might be left behind leaving the surface smooth.
Although it is a popular option, HASL may not be well-suited to fine pitch components because of nonuniform surfaces.
2. ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold):
ENIG is one of the most common surface finishes because it gives good solderability and a flat finish.
The procedure includes applying a thin layer of electroless nickel and immersion gold to the copper traces.
ENIG is appropriate for use in fine-pitch component applications and provides good corrosion protection.
3. OSP (Organic Solderability Preservative):
OSP is a surface finish in which an organic thin layer on the copper traces protects it from oxidation.
It offers planarity and is ecofriendly, but it does so with limited shelf life, which may not be compatible for repetitive reflow processes.
4. Immersion Silver:
Immersion silver is a process of coating the exposed copper surface with another layer made from silver.
It offers excellent solderability and is quite often used for applications where ENIG may be too much on the side of cost.
5. Immersion Tin:
Immersion tin is a circuit surface finish in which thin layer of tin gets applied directly on the copper traces.
It is low-cost, and it renders a smooth surface but may be susceptible to handling and storage.
6. Lead-Free HASL:
The lead-free HASL is a version of the traditional hasl, substituting its use as solder material with lead free.
It is an environmentally sound product but could have some issues when it comes to flatness and shelf life.
7. Hard Gold and Soft Gold:
Gold plating is a common treatment in connectors and applications where there are repeated cycles of connecting-disconnecting.
This is because hard gold with a thicker layer has more durability but can be costly while soft-gold suits applications that don’t experience much wear and tear.
The value of surface finish is determined by factors that include the application, component density among others. Every surface treatment has its merits and drawbacks, and choosing the right one is essential to overall performance as well as reliability of PCB.
Significance of a PCB surface finish
Surface finishes on a printed circuit board (PCB) have great bearing in the performance, dependability and durability of electronic appliances.
It acts as an essential boundary between the bare copper tracks on the PCB and components that are soldered to it. Here are some key aspects highlighting the significance of a PCB surface finish:
1. Corrosion Resistance:
PCBs corrode in humidity or harsh environments. The surface finish functions as a coat that prevents the long-term oxidation and corrosion of copper traces. This is essential in order to preserve the electrical performance of the PCB.
2. Solderability:
The solderability of the surface means its ability to form a lasting and reliable joint when assembled. Depending on the surface finish used, solderability may vary for soldering difficulty; correlation with assembly efficacy and quality among other factors is affected as well.
3. Flatness and Planarity:
The surface finish contributes to the production of a flat even plane on the PCB. This is especially crucial in the case of fine-pitch leads components and for securing high quality soldering during mounting. Flatness leads to better electrical performance and the simplification of manufacture.
4. Compatibility with Components:
The surface finish helps to produce a level and planar PCB. This is more crucial for fine-pitch lead components and warranting through soldering in assembly. Flatness increases the electrical properties and improves production.
5. Environmental Considerations:
A PCB’s performance can be affected by environmental factors such as moisture, temperature changes and chemical substances. Due to the environmental conditions that the PCB is expected to withstand, a suitable surface finish must be chosen in order for it be long-term reliable.
6. Multiple Reflow Cycles:
In the applications with multiple cycles of reflow soldering on PCBs, this surface finish should be strong enough to endure these activities without significant degradation. Certain finishes, such as ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold), are renowned for withstanding multiple reflow cycles.
7. Lead-Free Compliance:
Based on the stricter environmental regulations, a lead-free finish is usually required to prevent hazardous substances in most cases. Alternatives like lead-free HASL or ENIG are considerate and can be environmentally friendly.
8. Connector Reliability:
In applications where connectors are frequently plugged and unplugged, the type of surface finishing becomes essential. Hard gold or soft gold finishes provide quite good durability and reliable performance in connector applications.
Overall, to provide superior solderability without corrosion and flatness along with compatibility with any component or its assembly process is the main reason why PCB surface finish conditions are significant.
Since the requirements of an application, its surroundings and manufacturing methods should be reviewed thoroughly where surface finishes are concerned to achieve optimal PCB performance and reliability.
What are the types of PCB surface finish and their advantages and disadvantages?
It is also worth mentioning that printed circuit board surface finishes play as an important role when it comes to ensuring the performance and reliability of electronics devices besides there are different types withs their advantages and disadvantages which also the pcb surface finishes.
Hot Air Solder Leveling (HASL)
HASL is relatively low cost and also has very good adhesion; these are some of the reasons why it is widely used. On the other hand, its rough topography may not be appropriate for tiny pitch components.
Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold (ENIG)
Yet another broadly applied finish that is great in terms of corrosion protection and solder ability and surface coating. The ENIG is more expensive but is better for fine-pitch components also ENIG you can also see the surface coating
Organic Solderability Preservative (OSP)
Includes coating the copper surface with a thin layer of organic material. OSP has an advantage of being environmentally friendly and cost-effective; however, its shelf life is limited because it demands careful handling.
Immersion Tin (ISn)
It provides a level surface and is suitable for the incorporation of fine-pitch components but oxidizes easily.
Immersion Silver (IAg)
Offers superior solderability with a flat finish, but it is prone to tarnish quickly and has limited storage time. The selection of the most suitable surface finish requires consideration based on cost, nature of components and application requirements.
Thus rooting a careful deliberation over each posture’s merits when used in different circumstances
What is immersion gold plating and the advantages and disadvantages?
The surface finish of immersion gold plating is used in PCB manufacturing or pcb surface finishes. It is also referred to as Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold (ENIG), where gold deposits are put on the exposed copper surfaces of PCB using a series of chemical reactions.
Advantages of Immersion Gold Plating:
1. Corrosion Resistance:
Immersion gold provides high corrosion protection, this ensures that the PCB is long lasting in various environments.
2. Solderability:
The gold layer improves solderability of the PCB, enhancing assembly process with components soldering.
3. Flat Surface:
You can see the flat surface to the ENIG offers a level flatness and planarity to the flat surface which is compatible with the use of fine-pitch components under SMT technology which you can see to the flat surface.
4. Good for Multiple Reflows:
Immersion gold works well for applications that require several reflow soldering processes and retains its tinning property during multiple assembly cycles.
5. Fine-Pitch Component Compatibility:
Because of its smooth and even surface the ENIG is perfect for usage with PCBs equipped by small-pitch components where absolute soldering accuracy matters.
Disadvantages of Immersion Gold Plating:
1. Cost: Immersion gold is costlier than surface finishes such as Hot Air Solder Leveling (HASL).
2. Thickness Limitations: The gold film is very thin, which may not be appropriate for applications that would need a thicker coating. This limitation may even impact the longevity in severe situations.
3. Black Pad Phenomenon: There are circumstances under which an effect called a “black pad” can occur, the nickel layer that lies underneath corrodes causing solder joint reliability problems. Manufacturing practices and quality control measures are necessary to address this threat.
4. Sensitive to Handling: PCBs treated with ENIG can be easily damaged by traffic in the assembly process. Rigorous compliance with the appropriate handling procedures is important to prevent any issues.
Briefly, immersion gold is one of the most widespread surface finishes with outstanding corrosion resistance and soldering performance as well as application capability for small-pitch elements.
Its higher price is offset by numerous advantages, therefore making it one of the preferred options for applications where these features are essential some have uneven surfaces.
The value of immersion gold plating can only be fully achieved by careful handling and reliable quality control measures to counteract any weaknesses this process might have.
Conclusion
To summarize, the different types of PCB finishing play an important role in ensuring high performance and reliability for electronic products.
Every surface finish – HASL, ENIG finite metal layer (FML™), OSP coating, ISn and IAg have their own pros and cons.
The surface finish selection depends on the application needs, cost constraints and type of components used some they will use flat surface requirements some have uneven surface and some also hasl surface finish with durable surface. HASL is a cost-effective, preferred solution since ENIG has better corrosion and solderability properties.
OSP provides Eco friendly solution along with Immersion Tin and Silver offer planar surface for fine-pitch components which you can also see the solderable surface and the metallic surface finishes some are expensive pcb surface finish or pcb surface finish types.
More refined knowledge about such finishes enables manufacturers to make the right choices, so that PCBs are reliable and functional for whatever particular application of electronics they were made.